|
What is the difference
between an Index, and Abstract and a Full-text Database?
The information in
library databases comes in different formats. Some databases,
such as MLA (Modern Language Association) provide only citations for
information sources, and specific words that describe the information in
the source.
They are called Indexes.
Index Database:
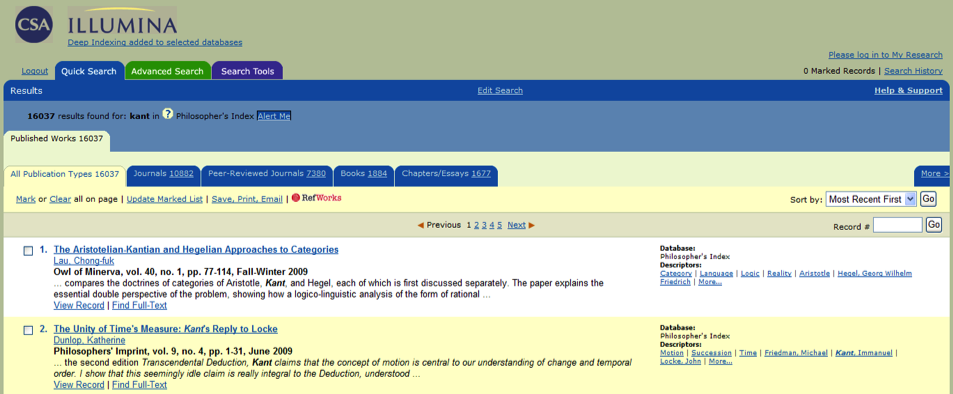
(click to enlarge image)
Other databases
provide more information. In addition to citations, they might include
abstracts (a short description of what a work is about) and thus are
called Index/Abstract databases. By reading
an abstract, you can often get a sense of whether an item will be
useful in your research. One example of this kind
of database is ERIC, which is provided by the Education Resource
Information Center, a subdivision of the Department of Education. Many index/abstract databases link to full text in other databases the Library subscribes to.
Index/Abstract
Database:
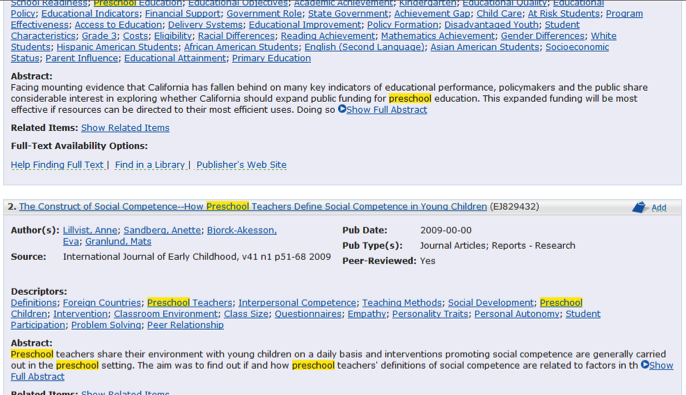
(click to enlarge image)
Lastly, there are
databases, such as Lexis-Nexis, that provide full-text access
to articles. These full-text databases provide citations and
abstracts as well.
Full-Text
Database:
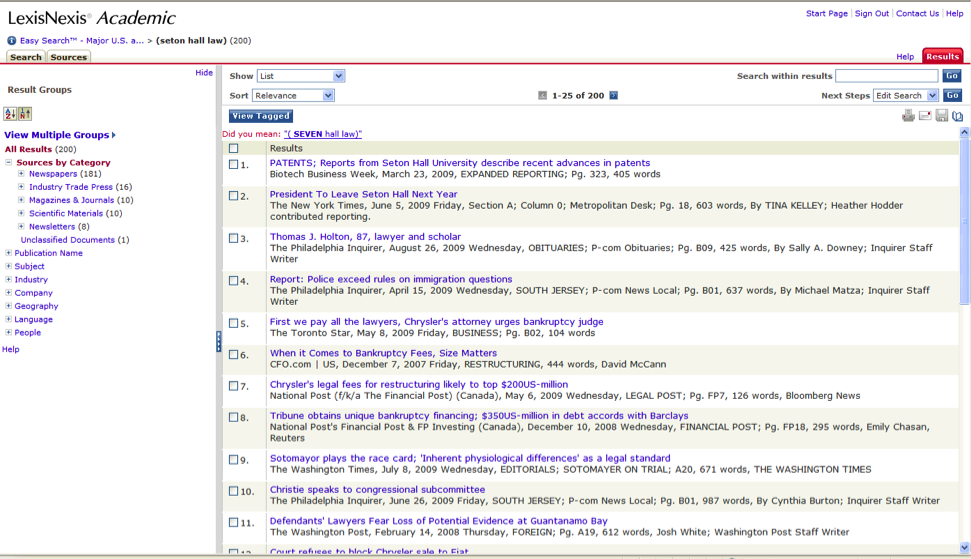
(click to enlarge image)
|